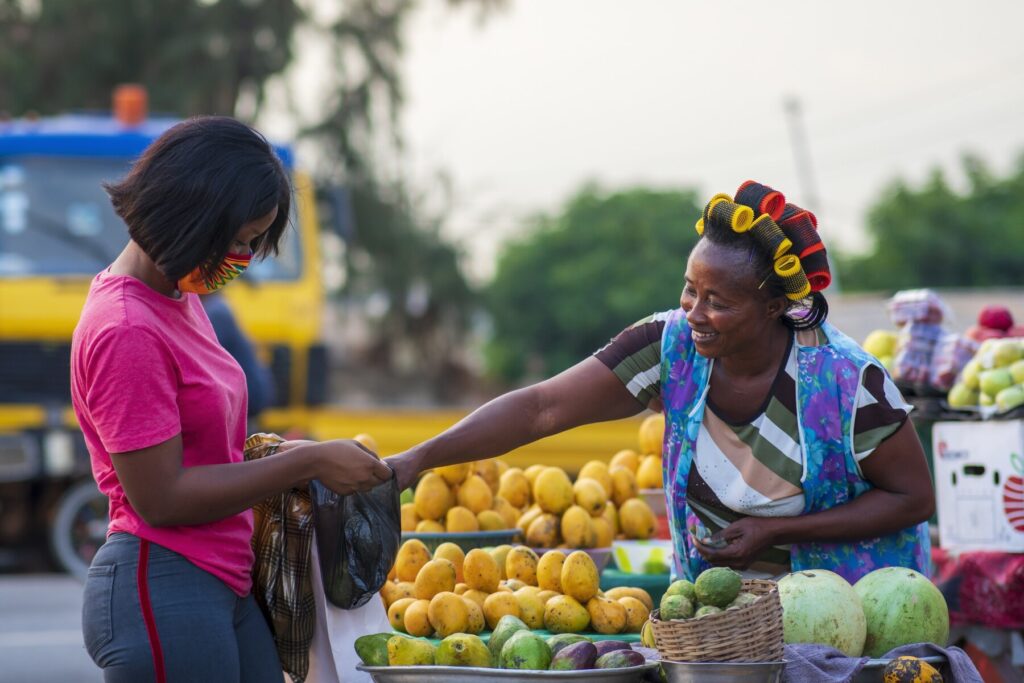
Author: Peace
Acknowledging and understanding the linkages between the formal and informal sectors are important for creating policies that improve livelihoods, foster entrepreneurship, and support sustainable economic growth across both sectors. Fusing these sectors effectively can lead to a more robust and inclusive economy.
The formal and informal sectors of an economy are interlinked in various ways, often complementing each other and contributing to overall economic activity.
Fitstly, the informal sector often serves as a source of employment for many individuals who may not find opportunities in the formal sector. People seeking temporary work or transitioning between jobs often find employment in the informal sector.
Supply Chain and Inputs: The formal sector frequently relies on the informal sector for the supply of raw materials, goods, or services. Small-scale producers or vendors in the informal sector often provide inputs to larger formal sector industries.
Distribution Networks: Informal sector traders and distributors often play a significant role in distributing products manufactured by the formal sector. They may act as intermediaries, reaching markets or areas that formal sector distributors might not access easily.
Innovation and Adaptability: The informal sector is known for its flexibility and adaptability to market changes. It often serves as a breeding ground for entrepreneurship, innovation, and testing new products or services before they transition into the formal economy.
Social Safety Net: In many cases, the informal sector acts as a safety net for individuals during economic downturns or times of unemployment. People may engage in informal activities to sustain themselves when formal employment opportunities are scarce.
Economic Growth and Contribution: The informal sector, while not always captured in official statistics, contributes significantly to economic growth through its role in employment generation, production, and overall economic activity.
Policy Implications: Recognizing the linkages between the two sectors is essential for policymakers to create policies that support and integrate the informal sector into formal structures, offering opportunities for growth, improving working conditions, and promoting financial inclusion.
